Understanding the Beach Chair Position: What Is Beach Chair Position In Surgery
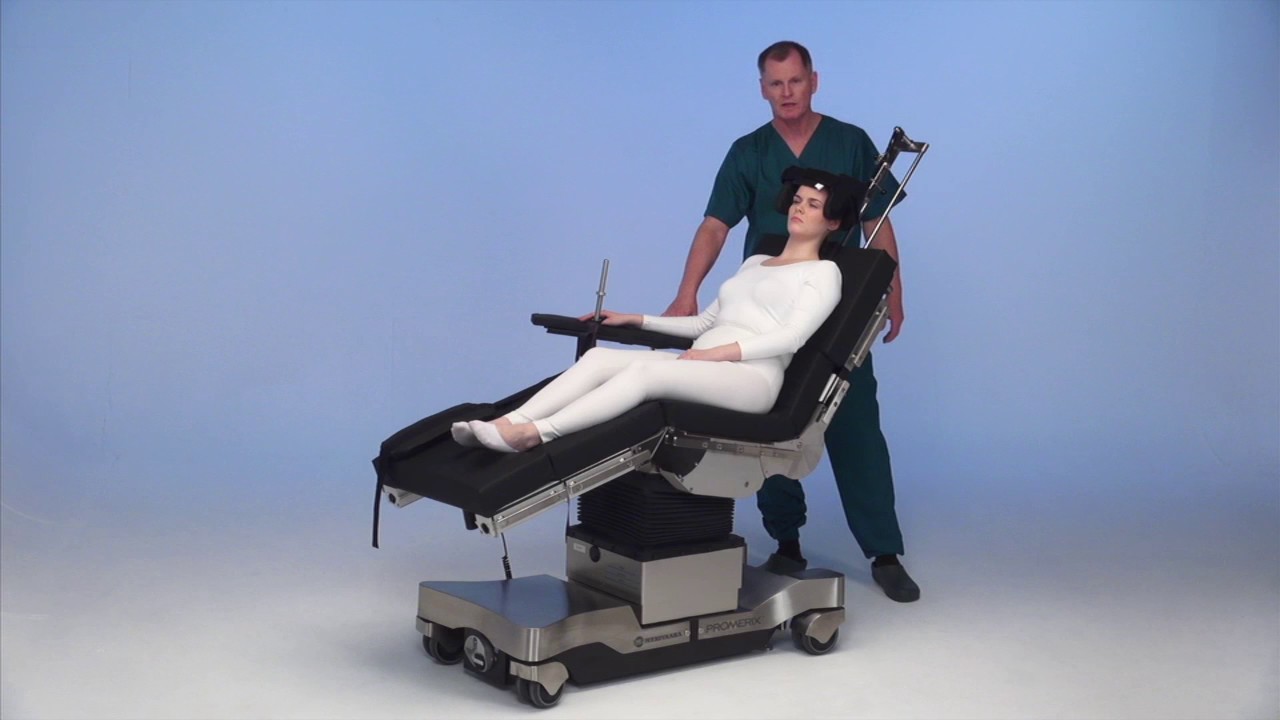
The beach chair position, also known as the semi-sitting or Fowler’s position, is a surgical positioning technique that elevates the patient’s upper body to a reclining angle. This position is frequently used in various surgical procedures, particularly those involving the head, neck, chest, and upper abdomen.
Patient Positioning
The beach chair position involves carefully positioning the patient’s body and limbs to ensure optimal surgical access, patient comfort, and safety. The patient is typically placed on a specialized operating table with adjustable sections. The table is then tilted to elevate the patient’s upper body to a reclining angle, typically between 30 and 60 degrees. The patient’s legs are typically extended and supported by footrests, while the arms are placed on armrests or secured with straps to prevent movement during the procedure. The patient’s head is often supported by a headrest or a specialized head holder, depending on the surgical procedure.
Equipment and Setup
To facilitate the beach chair position, a specialized operating table with adjustable sections is essential. These tables allow for precise control of the patient’s positioning and provide flexibility for different surgical procedures. Additional equipment includes:
- Footrests: Provide support for the patient’s legs, ensuring proper alignment and comfort.
- Armrests: Securely support the patient’s arms, preventing movement and ensuring comfort.
- Headrest or Head Holder: Stabilize the patient’s head, ensuring proper alignment and preventing movement.
- Straps and Padding: Used to secure the patient’s body and limbs, ensuring safety and minimizing movement during the procedure.
- Monitoring Equipment: Essential for tracking vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation.
Benefits and Drawbacks
The beach chair position offers several advantages, including:
- Improved Surgical Access: The elevated position provides surgeons with better access to the surgical site, particularly for procedures involving the head, neck, chest, and upper abdomen.
- Enhanced Visualization: The upright position allows for better visualization of the surgical field, facilitating more precise and efficient surgery.
- Reduced Venous Pressure: The reclining angle can help reduce venous pressure in the head and neck, minimizing the risk of swelling and improving blood flow.
- Improved Respiratory Function: The upright position can improve lung capacity and facilitate better ventilation, particularly in patients with respiratory issues.
However, the beach chair position also has some potential drawbacks:
- Increased Risk of Venous Air Embolism: The upright position can increase the risk of venous air embolism, a serious condition where air enters the bloodstream.
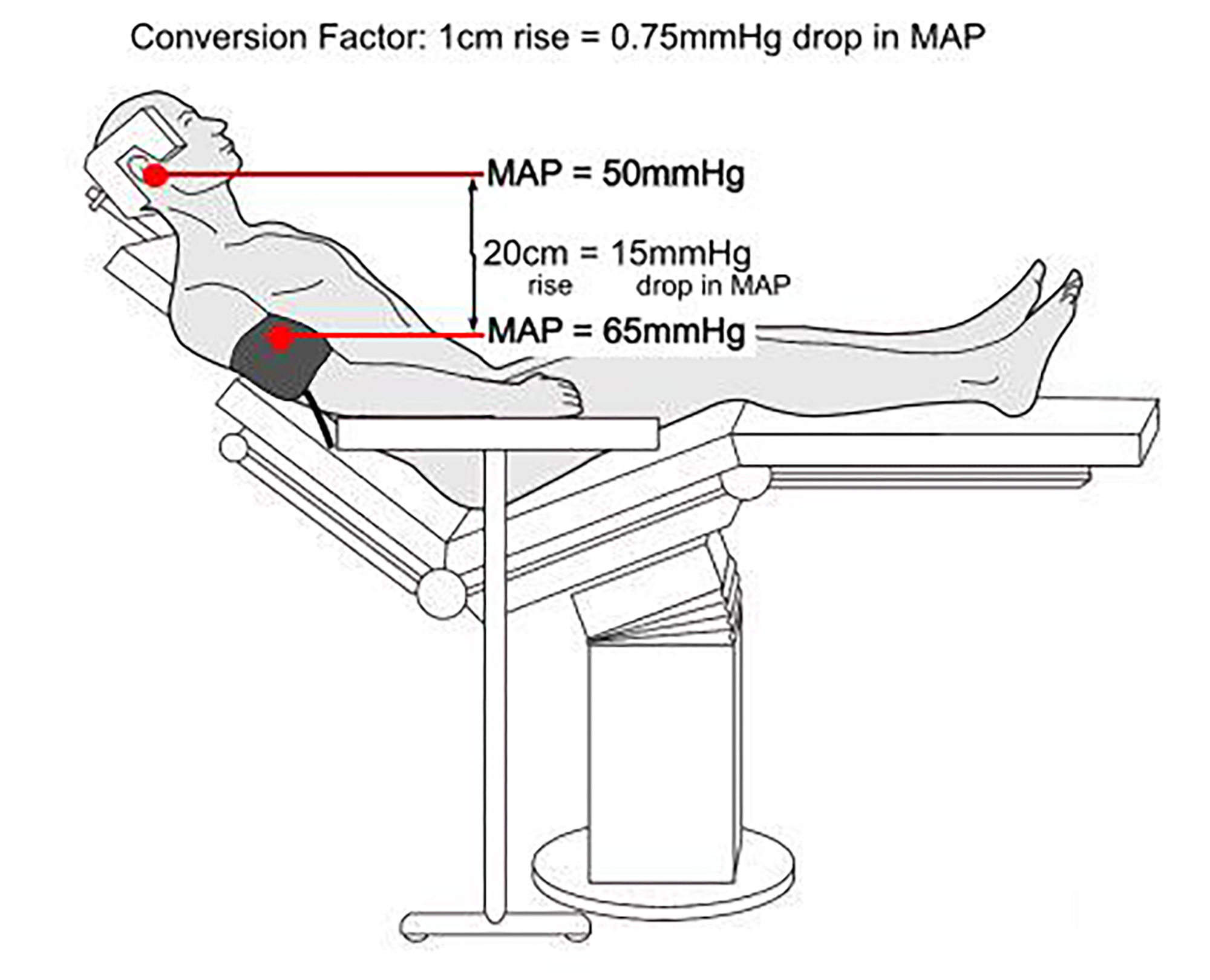
- Potential for Hypotension: The reclining angle can cause a decrease in blood pressure, particularly in patients with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions.
- Limited Access to the Lower Abdomen: The elevated position can make access to the lower abdomen more challenging, limiting its use for certain procedures.
Procedure and Considerations
Placing a patient in the beach chair position requires a systematic approach to ensure patient safety and comfort throughout the surgical procedure. This involves careful positioning, monitoring, and meticulous attention to potential complications.
Positioning the Patient
The beach chair position involves carefully positioning the patient in a semi-reclined position with their head elevated. This requires a specialized surgical table with adjustable sections to accommodate the desired angle. The procedure typically involves the following steps:
- Preparation: Before positioning the patient, the surgical team should gather all necessary equipment, including padding, straps, and monitoring devices. The patient’s skin should be cleansed and prepped to minimize the risk of infection.
- Positioning the Patient: The patient is placed on the surgical table in a supine position. The table is then adjusted to elevate the head and torso, creating the beach chair angle. The angle can vary depending on the surgical procedure being performed. For example, for procedures involving the head and neck, a steeper angle may be required.
- Securing the Patient: Once the desired angle is achieved, the patient is secured using straps and padding to prevent movement and maintain stability. Padding is essential to protect bony prominences and reduce pressure points.
- Monitoring: Throughout the procedure, vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation are closely monitored to ensure patient safety.
Precautions and Safety Measures, What is beach chair position in surgery
Maintaining patient safety and comfort is paramount when utilizing the beach chair position. This requires careful attention to potential complications and the implementation of preventive measures:
- Airway Management: The elevated head position can affect airway patency, especially in patients with pre-existing respiratory conditions. Maintaining a clear airway is essential, and the use of an oral or nasal airway may be necessary.
- Cardiovascular Considerations: The beach chair position can affect blood pressure and circulation. Close monitoring of vital signs is crucial, and adjustments to the position may be necessary to maintain hemodynamic stability.
- Pressure Points: Prolonged pressure on bony prominences can lead to skin breakdown and tissue damage. Padding and frequent repositioning are essential to prevent these complications.
- Nerve Compression: The beach chair position can compress nerves, especially in the upper extremities. Proper padding and positioning are crucial to prevent nerve injury.
Potential Complications
While the beach chair position is a valuable tool in surgical procedures, it can be associated with potential complications:
- Airway Obstruction: The elevated head position can make it difficult for the patient to breathe, particularly in those with pre-existing respiratory conditions.
- Hypotension: The beach chair position can cause a drop in blood pressure due to reduced venous return to the heart.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Prolonged immobility in the beach chair position can increase the risk of blood clots forming in the legs.
- Skin Breakdown: Pressure on bony prominences can lead to skin breakdown and ulcers.
- Nerve Injury: Nerve compression can occur, leading to pain, numbness, or weakness in the extremities.
Managing Patient Discomfort and Pain
Patient comfort is essential throughout the surgical procedure. Strategies for managing discomfort and pain in the beach chair position include:
- Padding: Using adequate padding under pressure points can minimize discomfort and reduce the risk of skin breakdown.
- Positioning: Adjusting the position of the patient’s arms and legs can alleviate pressure on nerves and improve circulation.
- Pain Management: Analgesics can be administered to manage pain and improve patient comfort.
- Communication: Open communication with the patient is essential to identify and address any discomfort or pain.
Variations and Applications

The beach chair position, with its versatility and adaptability, lends itself to several variations, each tailored to specific surgical needs and anatomical considerations. These variations not only enhance patient comfort and access but also minimize risks and optimize surgical outcomes.
Variations of the Beach Chair Position
The versatility of the beach chair position lies in its ability to be modified for various surgical procedures. Common variations include:
- Reverse Trendelenburg: In this variation, the patient’s head is elevated, and the feet are lower than the head. This position promotes venous return and helps manage fluid shifts during surgeries involving the head and neck, such as tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy. It is also used in laparoscopic procedures involving the upper abdomen, as it facilitates visualization and access.
- Trendelenburg: This variation elevates the patient’s legs, promoting venous return and reducing pressure on the inferior vena cava. It is often used in surgeries involving the lower abdomen and pelvis, such as hysterectomy and colorectal surgery.
- Lateral Beach Chair: This variation involves positioning the patient on their side, with the head elevated and the back slightly angled. This is particularly useful for surgeries involving the spine, chest, and kidney, as it allows for optimal exposure and access.
Common Surgical Procedures
The beach chair position is frequently employed in a wide range of surgical specialties, including:
- Otolaryngology: Tonsillectomy, adenoidectomy, and ear surgery.
- General Surgery: Laparoscopic procedures involving the upper abdomen, such as cholecystectomy and hernia repair.
- Gynecology: Hysterectomy, laparoscopic procedures involving the pelvis, and vaginal surgery.
- Urology: Kidney surgery, bladder surgery, and prostate surgery.
- Orthopedics: Spine surgery, shoulder surgery, and hip surgery.
Comparison with Other Positions
The beach chair position offers distinct advantages over other positions for similar procedures. For example, compared to the supine position, the beach chair position provides:
- Improved Visualization: The head elevation and slight backward tilt facilitate better visualization of the surgical field, especially in surgeries involving the head, neck, and upper abdomen.
- Enhanced Access: The angled position provides better access to the surgical site, especially in procedures involving the chest, abdomen, and pelvis.
- Reduced Risk of Pulmonary Complications: The elevated head position helps prevent aspiration and improves lung ventilation.
Advantages and Disadvantages in Different Specialties
The following table summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of the beach chair position in various surgical specialties:
| Specialty | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Otolaryngology | Improved visualization of the head and neck, reduced risk of aspiration. | Limited access to the back of the neck. |
| General Surgery | Enhanced access to the upper abdomen, improved visualization for laparoscopic procedures. | May cause pressure on the inferior vena cava, potential for hypotension. |
| Gynecology | Improved visualization of the pelvic organs, enhanced access for laparoscopic procedures. | May cause pressure on the inferior vena cava, potential for hypotension. |
| Urology | Enhanced access to the kidneys, bladder, and prostate. | May cause pressure on the inferior vena cava, potential for hypotension. |
| Orthopedics | Improved visualization and access for spine surgery, shoulder surgery, and hip surgery. | May cause pressure on the inferior vena cava, potential for hypotension. |
What is beach chair position in surgery – The “beach chair position” in surgery, where the patient is reclined with their legs elevated, might seem like a relaxing beach day, but it’s actually a vital position for certain procedures. It’s a far cry from lounging on a coleman treklite coolerpack beach chair , but the position helps surgeons access specific areas of the body and ensures proper blood flow during surgery.
Just like the right chair can make a difference on the beach, the right surgical position is crucial for a successful outcome.
In surgery, the beach chair position is a comfortable and versatile option for certain procedures. It allows for good access to the back, neck, and shoulders. Just like relaxing in a coors light beach chair on a sunny day, the beach chair position helps patients feel at ease during their surgery.
This position is often used for procedures involving the spine, head, and neck, allowing surgeons to work with precision and care.
